+86 186 3170 8948
+86 186 3170 8948
Oct. 15, 2025
Gate Valves serve to isolate flow, while a Pressure Reducing Valve maintains system pressure. Yaxing Valve engineers both types to meet demanding industrial requirements. Gate valves provide reliable on/off control, making them ideal for isolating flow in pipelines across various industries. Pressure reducing valves maintain consistent downstream pressure, ensuring safe operation in systems with fluctuating inlet pressures. Understanding the distinction ensures safe and efficient fluid control in complex environments.
Gate valves serve as essential components in industrial fluid control systems. These valves use a wedge-shaped disk that moves up and down to start or stop the flow of liquids or gases. When operators need a device for complete shutoff, gate valves provide a reliable solution. Their straightforward design makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from water supply lines to chemical processing plants.
A Gate Valve operates by raising or lowering its internal gate. When the gate lifts, fluid flows freely through the valve without obstruction. Lowering the gate seals the passage, stopping all movement of the medium. This mechanism ensures efficient on/off control. The following table summarizes the two main operational states:
Operation State | Description |
|---|---|
Fully Open | The gate is entirely raised, allowing fluid to flow freely without obstruction. |
Fully Closed | The gate is lowered into the seat, sealing the flow path and preventing fluid movement. |
Gate valves excel in systems that require straight-line flow and minimal pressure drop. Their design supports bidirectional sealing, which enhances system safety.
Many industries rely on gate valves for critical operations. In oil and gas, these valves regulate flow in pipelines and drilling rigs. Chemical processing plants use gate valves to control aggressive substances. Water treatment facilities depend on them for managing water flow and ensuring public safety. Mining operations use gate valves for mineral processing and hydraulic systems. Marine sectors install gate valves to control ballast water and fuel systems. Operators value their ability to handle high pressures, temperatures, and corrosive environments. Gate valves remain a top choice for efficient shutoff and isolation across diverse industrial sectors.
A pressure reducing valve is a specialized device that controls and maintains a set downstream pressure in fluid systems. Industry standards define these valves by their construction, coding, and performance requirements. The table below summarizes key specifications:
Specification Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Purpose | Establishes construction, coding, and performance requirements for pressure-reducing valves in water systems on ships. |
Pressure Settings | Limited to discharge pressure settings of 200 psig (1379 kPa) and below. |
Valve Types | Includes pressurized spring chamber type (Type I) and unpressurized spring chamber type (Type II). |
Testing Requirements | Valves must conform to hydrostatic proof, seat tightness, set pressure limits, and capacity testing. |
Pressure reducing valves stabilize downstream pressure even when inlet pressure fluctuates. The valve body regulates flow, while an internal V port throttling plug provides precise control and reduces noise. The pilot regulator acts as the brain, working with the needle valve to maintain consistent pressure. The following list outlines the main steps in operation:
● The valve body stabilizes flow and regulates pressure.
● The V port throttling plug ensures accurate flow and pressure control.
● The pilot regulator determines water flow between the control chamber and maintains pressure.
A pressure reducing valve uses a spring-loaded diaphragm or piston to automatically adjust flow. When pressure rises, the diaphragm compresses the spring, partially closing the valve. When pressure drops, the diaphragm opens the valve further, allowing more flow.
Pressure reducing valves play a vital role in many industries. The table below highlights common applications:
Industry | Specific Process |
|---|---|
Potable Water Systems | Reduces water pressure to safe levels to prevent damage to water mains and appliances. |
Hydraulic Systems | Reduces fluid pressure to safe levels for system components in industrial applications. |
Pneumatic Systems | Maintains suitable pressure for pneumatic tools and equipment using compressed air. |
Gas Systems | Protects installations from dangerous pressures that could lead to leaks or explosions. |
Steam Systems | Ensures safe operation by regulating steam pressure in various applications. |
Gate valves and pressure reducing valves serve distinct roles in industrial systems. Gate valves isolate or allow full flow in a pipeline. Operators use them when they need to stop or start the movement of fluids completely. These valves do not regulate flow or pressure; they simply open or close the passage. Pressure reducing valves, on the other hand, maintain a set downstream pressure. They automatically adjust to changes in inlet pressure, ensuring that the system operates within safe limits. This function protects equipment and prevents damage from excessive pressure. Both types of valves contribute to system safety, but their core purposes differ.
The internal design of gate valves and pressure reducing valves reflects their unique functions. Gate valves feature a simple structure with a valve body, gate plate, and sealing ring. The gate moves up and down to block or permit flow. Pressure reducing valves have a more complex assembly, including a valve body, valve core, and spring mechanism. This design allows for precise pressure control.
Valve Type | Internal Components | Materials Used |
|---|---|---|
Gate Valve | Valve body, gate plate, sealing ring | Typically metal alloys |
Pressure Reducing Valve | Valve body, valve core, spring | Often metal and plastic |
Material selection plays a critical role in durability and suitability for different fluids. Yaxing Valve offers gate valves in stainless steel, brass, cast iron, and ductile iron. Each material provides specific benefits:
Material Type | Corrosion Resistance | Durability | Pressure Rating | Temperature Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Stainless Steel | High | Moderate | High | High |
Brass | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
Low | High | Moderate | Low | |
Ductile Iron | Moderate | High | High | Moderate |
Pressure reducing valves often use a combination of metals and plastics to balance strength and flexibility. Yaxing Valve ensures that all types of valves meet strict quality standards for industrial use.
Industries select gate valves when they require reliable isolation in pipelines. Water treatment plants, oil and gas facilities, and chemical processing units depend on these valves for shutoff tasks. Gate valves handle a wide range of fluids, including water, oil, gas, and corrosive chemicals. Their robust construction and bidirectional sealing make them suitable for demanding environments.
Pressure reducing valves find their place in systems where pressure control is essential. Potable water networks, hydraulic circuits, pneumatic tools, and steam systems all benefit from stable downstream pressure. These valves protect sensitive equipment and maintain operational safety. Yaxing Valve designs both types of valves to meet the needs of diverse industries, ensuring compatibility with various fluids and system requirements.
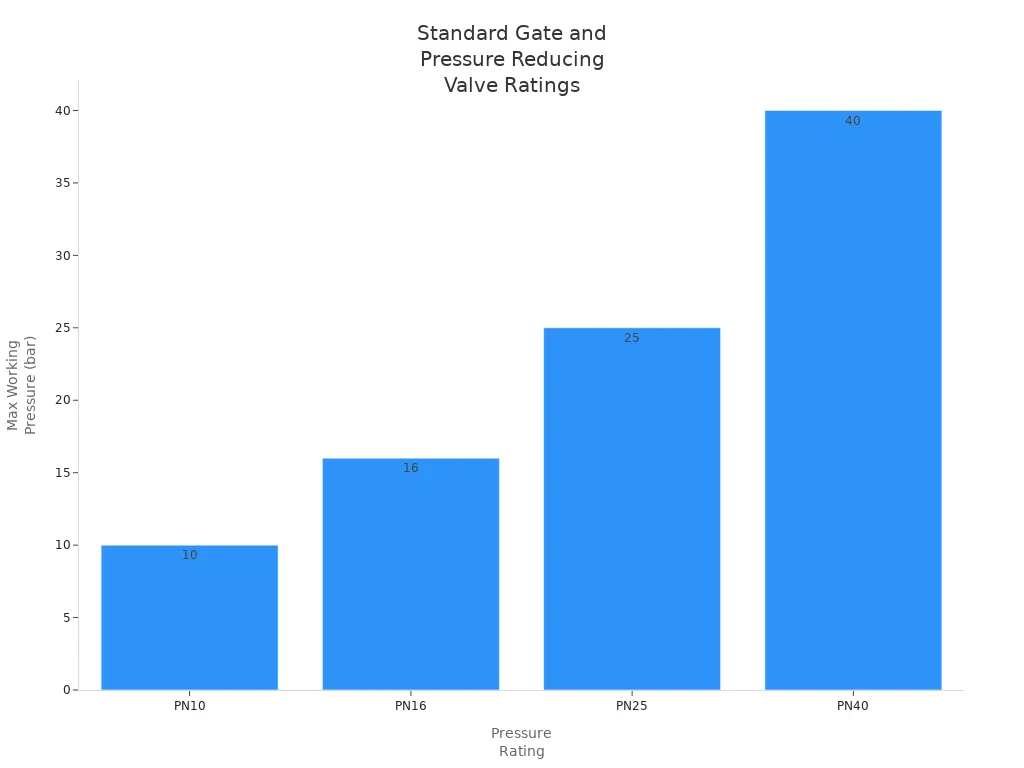
Performance metrics for gate valves and pressure reducing valves differ based on their intended use. Gate valves excel in providing minimal pressure drop when fully open. They support high-pressure ratings, with options such as PN10, PN16, PN25, and PN40. The following table summarizes standard pressure ratings:
Pressure Rating | Description |
|---|---|
PN10 | Maximum working pressure of 10 bar |
PN16 | Maximum working pressure of 16 bar |
PN25 | Maximum working pressure of 25 bar |
PN40 | Maximum working pressure of 40 bar |
For reference, gate valves and pressure reducing valves also comply with industry classes such as Class 150 (up to 285 psi at 20°C) and Class 300 (up to 740 psi at 20°C).
Material selection, structural design, and manufacturing quality all influence the pressure-bearing capacity of these types of valves.
Gate valves have evolved with technological advancements. Modern designs include automated actuators, smart monitoring systems, and advanced sealing technologies. These features improve safety, efficiency, and environmental compliance. Yaxing Valve incorporates these innovations, offering options like duplex steels and corrosion-resistant coatings for extended service life.
Pressure reducing valves also benefit from recent advancements. Smart technologies enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Enhanced safety features, energy-efficient designs, and electronic pressure regulators provide precise control and reliability. Yaxing Valve’s pressure reducing valves include easy maintenance features, fail-safe mechanisms, and customization for specific applications.
Gate valves provide reliable on/off control and suit high-pressure environments. Pressure reducing valves maintain safe system pressure. Yaxing Valve offers both solutions for industrial users.
Gate valves excel in straightforward shutoff tasks.
Pressure reducing valves ensure consistent downstream pressure.
Next post
Related Products
Botou Yaxing Fluid Equipment Co., Ltd. specializes in providing design, development, and manufacturing services for the water valve industry. We produce high-quality valve products.
+86 186 3170 8948
No.4 Road Botou Industrial Zone, Cangzhou City Hebei Province, China
Get Free Sample
 Privacy Policy
Privacy Policy